Ticket reselling can be a win-win situation. It can help fans who missed out on initial tickets enjoy the event, while offering a lucrative opportunity of profit for resellers. But like any other business, ticket reselling has its nuances, rules, and risks that you need to understand to do it right. In this guide, we will discuss how you should plan and the best tested tips you should follow when you think about:
- Understanding the market.
- Identifying events that can generate profitable resale.
- Buying tickets strategically: Where and when to buy can greatly affect the profit margin.
- Choosing reselling platforms.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Ticket Reselling (What Is Ticket Resale?)
- Ticket Scalping vs. Ticket Reselling
- What Are The Risks Involved In Ticket Reselling?
- What Events To Buy Tickets For?
- The Plan: 11 Tips to Start Reselling Tickets
- Is Reselling Concert and Event Tickets Profitable?
- Is It Legal To Resell Tickets For Profit?
Definition of Ticket Reselling (What Is Ticket Resale?)
Ticket reselling refers to the practice of purchasing tickets to concerts, sports games, theater shows and other events with the intent to resell them for a higher price on secondary marketplaces.
Resellers aim to generate a profit by selling the tickets they acquire at prices above what they originally paid. It provides a secondary market option for fans to obtain tickets to events that have limited quantities available from the primary seller and where demand for tickets exceeds supply.
Reasons for the existence of reselling tickets business include:
- Insufficient ticket releases by primary vendors.
- Extraordinarily high demand for hot events that sell out quickly.
While some view ticket reselling as an unethical business, others see it as providing necessary opportunities for more fans to get tickets in an undersupplied market.
Ticket Scalping vs. Ticket Reselling
| Ticket Scalping | Ticket Reselling |
|---|---|
| Selling tickets at prices significantly higher than the official ones, especially in shortage situations. | Purchasing tickets at face value and reselling them at a slightly higher price, often through official channels. |
| Reduces availability of tickets at face value, inflates market prices due to bulk buying. | Less impact on ticket availability; typically involves regulated and smaller markups. |
| Often illegal or highly regulated due to negative market impact. Varies by country. | Generally legal, operates within a more official and regulated framework. |
| High markup, often speculative. | Smaller markup, more aligned with market norms. |
| Subject to strict laws in many countries; some like Australia have specific laws to limit scalping. | Subject to standard commercial and consumer protection laws, less contentious than scalping. |
| Viewed negatively due to predatory pricing and market manipulation. | Generally accepted as a standard business practice. |
What Are The Risks Involved In Ticket Reselling?
Just like any other business, ticket reselling comes with a set of potential risks that a beginner needs to account for. Here’s an overview of the most common risks:
- Fraudulent tickets: Purchasing tickets from non-reputable sources increases the risk of buying fraudulent tickets. This can result in significant financial loss and damage to your reputation.
- Chargebacks: Sometimes, a customer may request a chargeback from their credit card company, leading to a loss of revenue for the reseller.
- Legal implications: As we’ve mentioned before, the legality of ticket reselling can vary by location and event. This makes it crucial to research and understand the legal restrictions applicable to your activities.
- Price Fluctuations: Value of concert or event tickets can fluctuate wildly depending on factors like artist popularity, venue capacity, and proximity to the event. That means the profit you expected to make when you originally purchased the tickets could shrink or even vanish.
- Unsold inventory: If you’re unable to sell all your tickets before it’s too late, you can end up incurring losses.
While these risks can seem intimidating, they are not insurmountable. With careful planning, thorough research, and meticulous execution, it’s possible to navigate the landscape of ticket reselling and turn a tidy profit.
Related: Top 5 Mistakes in the ticket reselling business.
What Events To Buy Tickets For?
Understanding the market and selecting the right events is the first step to a successful ticket reselling business. Here are some factors you need to consider before you choose your target events:
- Popularity and Demand: Focus on events with high demand and popularity. Concerts of renowned artists, major sports events, or exclusive theater shows often attract a lot of interest.
- Limited Availability: Events with limited ticket releases can create a lucrative resale market. The scarcity of tickets often drives up their value.
- Anticipate Trends and Holidays: Stay updated with upcoming tours, album releases, or sporting seasons. Predicting future hot events can give you a head start. Also prepare for holidays. New Year’s Eve events often have a high resale value.
- Analyze Historical Data: Analyze past events by the same artist, team, or show. Events that sold out quickly in the past are likely to do so again.
- Follow Local Events: Don’t overlook local events with a strong following. These can sometimes offer surprisingly good resale opportunities.
- Buy Annual Festival Tickets: Music and cultural festivals, especially those held annually, often see a surge in demand as the event approaches.
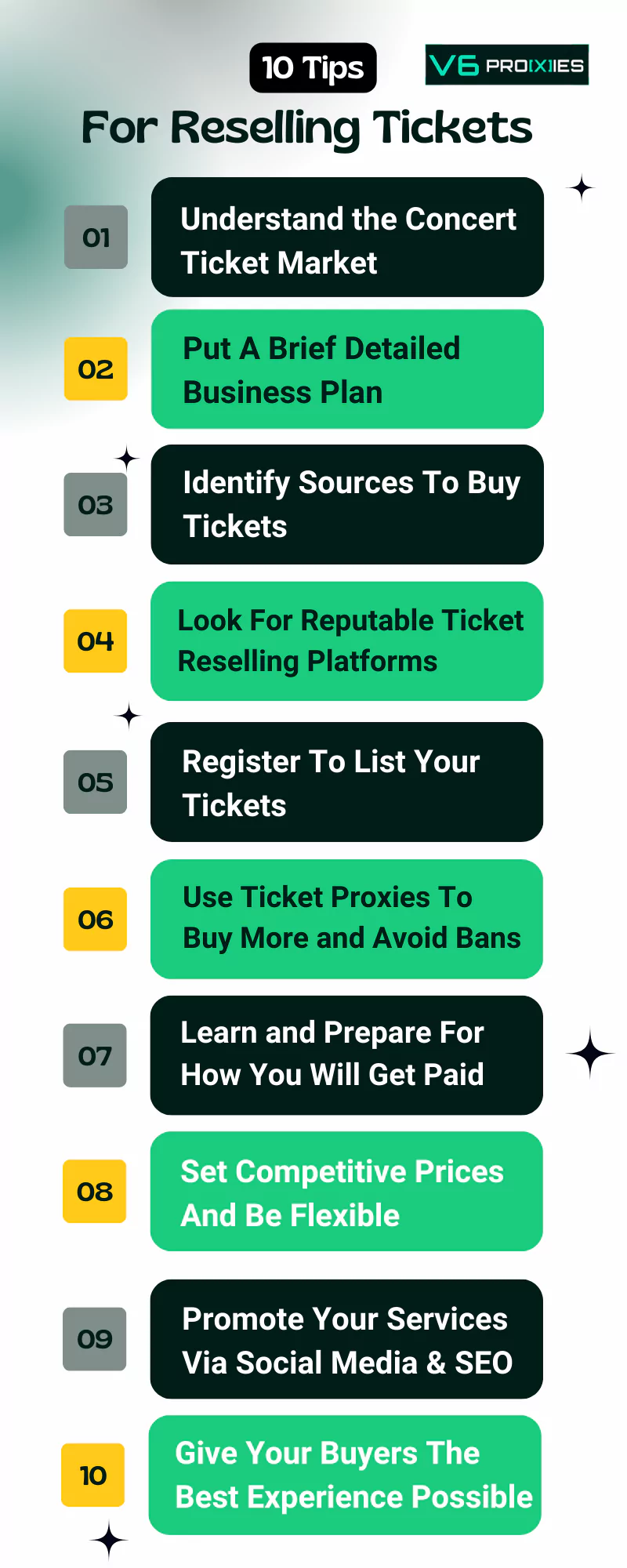
The Plan: 11 Tips to Start Reselling Tickets
1. Understand the Concert Ticket Market
Before diving into ticket reselling, gain a thorough understanding of the market. Research current trends, popular artists, venues, and typical ticket prices.
Understand peak seasons and factors that influence demand, such as artist popularity or event uniqueness. Familiarize yourself with different types of tickets and seating arrangements, as these can greatly affect resale value.
2. Put a Brief Business Plan
Create a concise business plan that outlines your objectives, target market, budget, and strategies. Research the legal aspects of ticket reselling in your area, including any licenses required.
Determine your initial investment and how much you’re willing to risk. Identify your target market—whether it’s fans of a particular music genre, sports enthusiasts, or theatergoers. Decide how you will market your services and think about your pricing strategy.
3. Find Tickets to Buy
Identify sources to buy tickets. This can include primary ticket sites, fan clubs, presales, or direct from venues. Stay updated with on-sale dates and times for high-demand events. Use alerts, notifications, and newsletters from ticketing platforms to stay ahead of the game.
4. Look For Reputable Ticket Reselling Platforms
Select reputable platforms for reselling your tickets. Consider factors like user base, fees, payment security, and market reach. Popular platforms include StubHub, Ticketmaster Resale, and reselling on AXS. Each platform has its policies and audience, so choose the ones that best fit your business model. You can find a complete review of the best ticket sites in our blog.
5. Register To List Your Tickets
Create accounts on your chosen ticket reselling platforms. Ensure your account details are accurate and complete. Familiarize yourself with the listing process, fees, and terms of service for each platform.
6. Use Ticket Proxies To Buy More and Avoid Bans
Consider using ticket proxies to circumvent restrictions on the number of tickets you can buy from a single IP address. Proxies can help you buy more tickets and reduce the risk of getting banned by ticket sites. You can learn all about them and buy them from V6proxies.
7. Learn How You Will Get Paid
Understand the payment process on each platform. Know when and how you’ll receive your earnings. Some platforms may hold your payment until after the event, while others might pay out sooner. Be aware of any fees or commissions that will be deducted.
8. Control Your Pricing
Set competitive prices for your tickets. Monitor the market to understand pricing trends for similar events. Factor in your costs and desired profit margin. Be flexible with your pricing strategy, adjusting prices based on demand and proximity to the event date.
9. Promote Your Services
Market your ticket reselling services. Use social media, online forums, reddit, and word-of-mouth to reach potential buyers. Consider creating an online store or blog to showcase your inventory and share insights about upcoming events.
10. Sell, Make Money and Improve Your Process
Once you start selling, track your sales and profits. Analyze which strategies are working and which aren’t. Use this information to refine your business model. Continuously look for ways to improve your buying strategies, pricing, and marketing efforts.
11. Give Your Buyers The Best Experience Possible
Focus on providing excellent customer service. Ensure the tickets are delivered on time and as described. Be responsive to customer inquiries and transparent in your dealings. Positive customer experiences can lead to repeat business and referrals, which are vital for long-term success in ticket reselling.
Is Reselling Concert and Event Tickets Profitable?
Reselling concert and event tickets can be profitable, especially for high-demand events where ticket availability is limited. Profit potential depends on factors like the popularity of the event, the scarcity of tickets, and the timing of the resale.
Is It Legal To Resell Tickets For Profit?
The legality of reselling tickets for profit varies depending on the jurisdiction. In many places, it is legal, especially when done through official channels or authorized resellers. However, some regions may have specific laws or restrictions on the resale of tickets, especially at prices significantly above face value. Always check local laws to ensure compliance.
Related Articles
- Top 10 Ticketmaster Alternatives (Buy & Resell Event Tickets)
- Ticketmaster Waiting Room: Top Tips to Beat the Queues
- Best 5 Ticketmaster Proxy Providers
- Can You Resell Tickets On Ticketmaster For A Higher Price?
- Can You Sell/List Tickets On Multiple Sites? (A 2024 Answer)
- Is Ticket Scalping Illegal? (Laws In Main SU State)
- What Is MAP Monitoring? [Track Your Pricing Compliance]
- Facebook Scraping 101 (Everything You Need for Success)
- How Do Ticket Scalpers Get Tickets Before Fans?
- What Are Demand Tickets On AXS? (2024)
- Can You Transfer Ticketmaster Tickets to StubHub? (2024)
- How To Resell Tickets On SeatGeek? (2024 Guide)
- Ticket Buying Bots Guide | 7 Questions and Answers
- How To Get Unblocked From Ticketmaster? [Easy Fixes 2024]
- How To Make Money With Web Scraping? (10+ Examples) (2024)
- Tags:
- Reselling, Ticketing proxies